
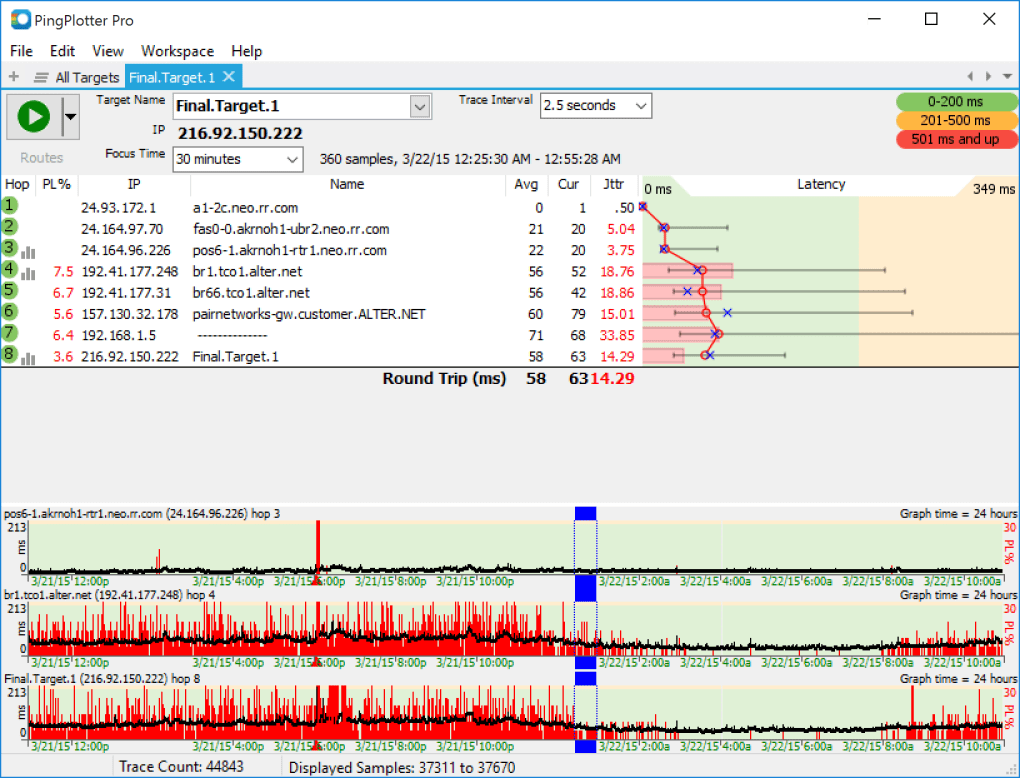
Traceroute, also called tracepath or tracert, is a TCP/IP network utility used to determine the path packets take from one IP address to another. Sometimes, a company's network security policy requires ping (ICMP Echo Reply) to be disabled on all devices to make them more difficult to be discovered by unauthorized persons. The ping command sends an ICMP Echo Request consisting of a single packet of data (often 32 or 56 bytes), and the host device should reply with an ICMP Echo Reply.
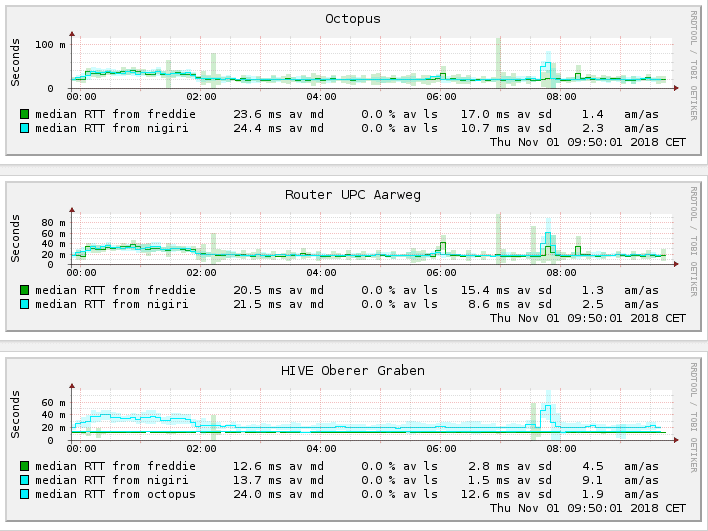
It serves two primary purposes: 1) to check if the host is available and 2) to measure how long the response takes. Higher Latency = Longer Delay.Ī ping is a signal sent to a host that requests a response. When one or more of these packets fails to reach their intended destinationĭescribes a delay that takes place during communication over a network (including the Internet) - usually measured in milliseconds.
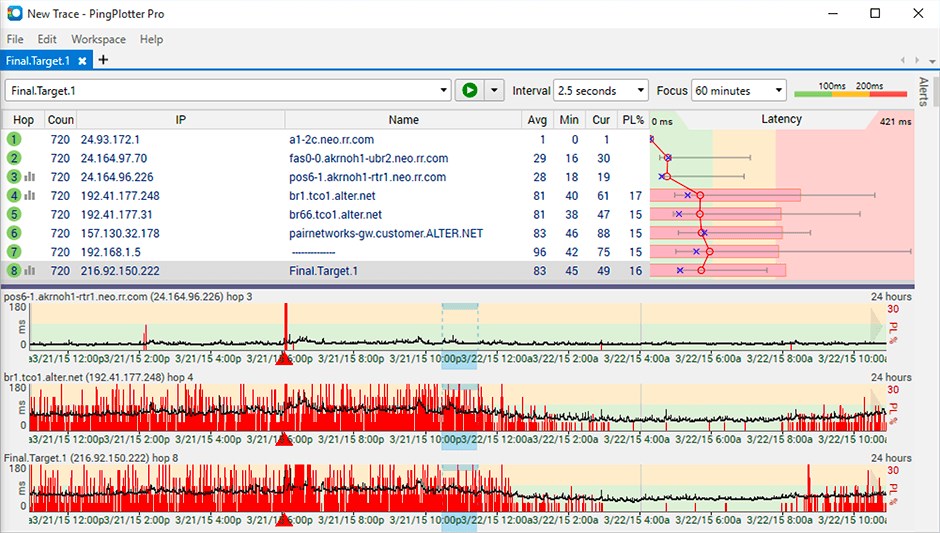
When the packets reach their destination, they are reassembled into a single file or other contiguous blocks of data. Similar to a real-life package, each packet includes a source and destination as well as the content (or data) being transferred. DefinitionsĪ packet is a small amount of data sent over a network, such as a LAN or the Internet. Finally, these things will all come together in the last section which will not only describe how PingPlotter works but hopefully, will enhance your understanding of network troubleshooting. We’ll start by defining some network terms, followed by a brief explanation of their concepts. Just like with every great invention, a lot of people want to know what makes PingPlotter tick - which is exactly what we aim to illustrate in this article! PingPlotter - How it really works Overview


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
